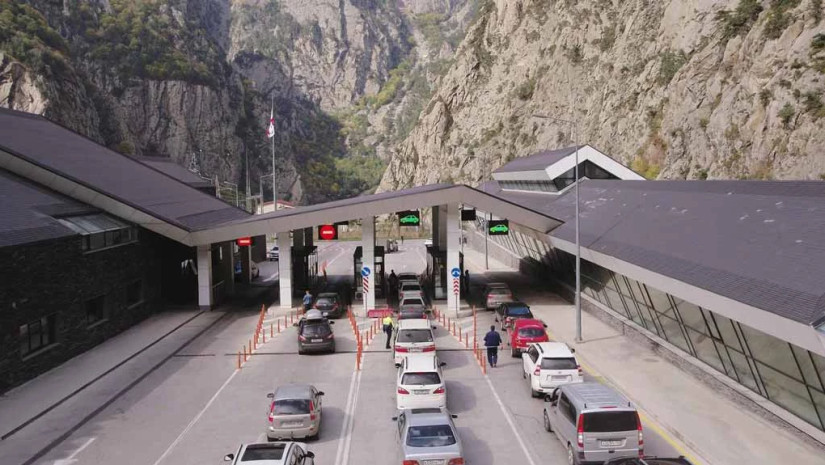
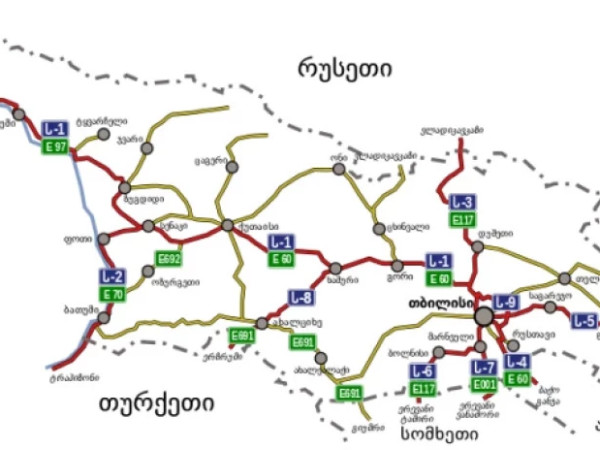
North Ossetian Telegram channels report that people have been allowed to pass passport control and walk across the Georgia-Russia border.
According to Ekho Kavkaza, earlier the border could be crossed only by vehicle or bike.
The information was confirmed by the press service of the FSB border service of North Ossetia, who noted that such a decision was made "for speed".
According to Ekho Kavkaza, the above reports that it is now possible to cross the border on foot were spread via the so-called Zemo Larsi chat and Tbilisi_life Telegram channel.